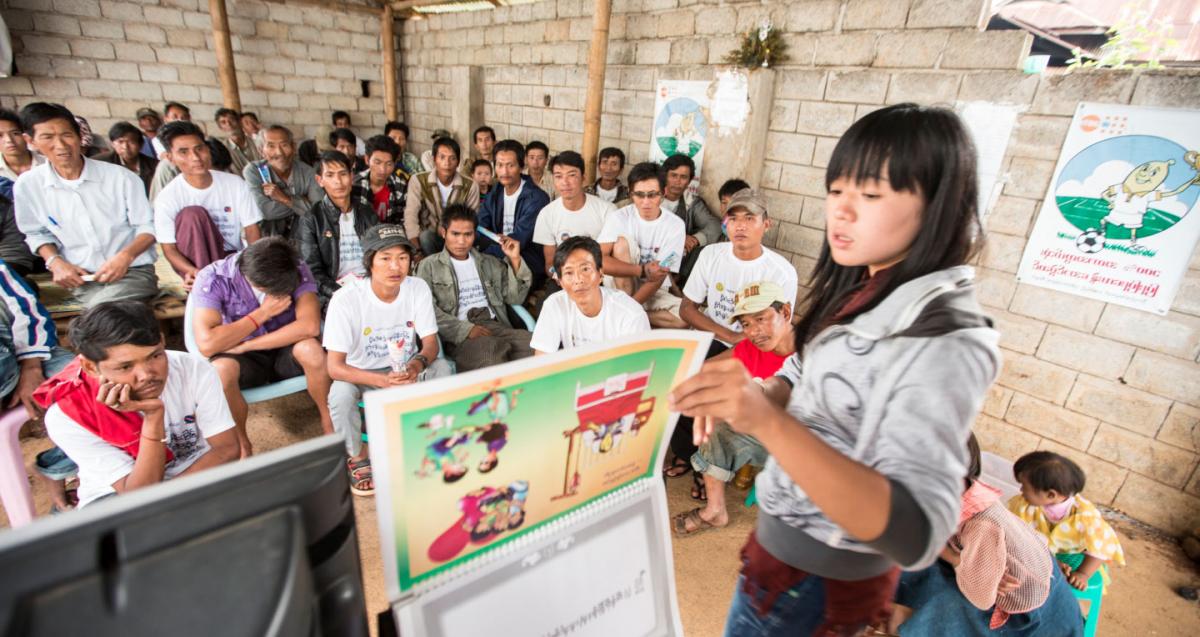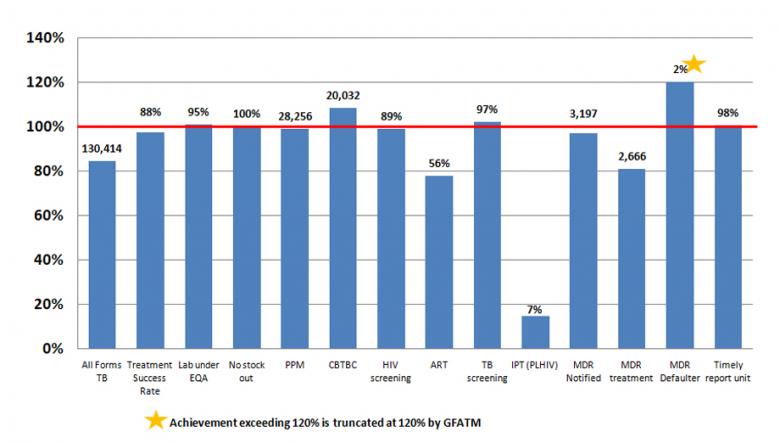
The cumulative results for Year 7 (NFM) are shown as a percentage of the annual target. TB–HIV indicator (collaborative sites) and MDR-TB treatment indicators are funded by GFATM and other donors, while the others are funded by GFATM only.
TB grant implementation has also shown progress, with 6 out of 14 reportable indicators either meeting or exceeding the annual targets by the end of 2017.
During the year, 130,414 (84% of the annual target) TB patients were notified and enrolled on treatment. The treatment success rate was 88 per cent.
To increase case notification, coordination has been increased with other service providers such as military hospitals, public and private hospitals, and non-governmental organizations working in border areas with the involvement of ethnic minority health workers.
To increase identification of hidden TB cases, mobile active case finding activities have been expanded among groups including prisoners, industrial workers, miners, migrant workers and people who inject drugs.
External quality assurance samples (quality control slides) from 425 of the 450 participating laboratories were sent for assessment and 403 of the 425 laboratories, or 95 per cent, (101% of target) met the quality control performance criteria.
Training and mentoring of upper and lower Myanmar TB laboratories, technical assistance and supportive supervision from WHO were crucial in achieving this result. Refresher training and close supervision is usually provided to the low performance townships.
In 2017, 3,197 (97%) multi-drug resistant TB (MDR-TB) cases were notified. Advocacy meetings were held and refresher training conducted on the new algorithm of the TB treatment guidelines. As a result, the programme was able to identify more cases than in the previous year. During the year, 2,666 (81% of target) MDR-TB patients were put on second-line treatment.
The new MDR-TB guidelines have been implemented since the beginning of this year, and training on the new algorithm of MDR-TB treatment has been conducted at the central and state/regional level, with an increase in the number of GeneXpert sites to 73 in 2017. Workshops and review meetings were conducted on strengthening the sputum transportation system for implementing partners.
During the year, 28,256 (99% of target) TB patients were referred and/or treated by partners implementing Public-Private-Mix (PPM) partnership approach. In 2017, the number of cases of all forms of TB notified by community volunteers through community-based TB care activities was 20,032, or 15 per cent (108% of target).
This year, 82,510, or 97 per cent (102% of target) of HIV patients were screened for TB during follow-up visits to the ART centre and decentralized sites.
During the year, 1,009, or 7 per cent (15%) of people living with HIV (PLHIV) newly enrolled in HIV care received isoniazid preventive therapy (IPT).
In 2017, only 49, or 2 per cent (120%) of MDR-TB patients who started treatment in the last 12 months were lost to follow-up during the first 6 months of the treatment, much lower than the programmatic limit of 3 per cent.
In order to ensure MDR-TB treatment adherence, the grant provided nutritional support to all registered MDR-TB patients, with routine health education messages included on MDR-TB.
This year, 98 per cent (355) of reporting units – comprised of 321 townships, 26 public hospitals, and 8 non-governmental organizations – submitted their reports (paper-based) in accordance with the national guidelines. The programme maintained its high performance, and robust recording and reporting system.
Over the year, the HIV test results of 89 per cent (115,838) of notified TB cases were recorded in the TB register, reaching close to the programmatic target of 90 per cent.
In 2017, all reporting units reported no stockout of first-line anti-TB drugs.


