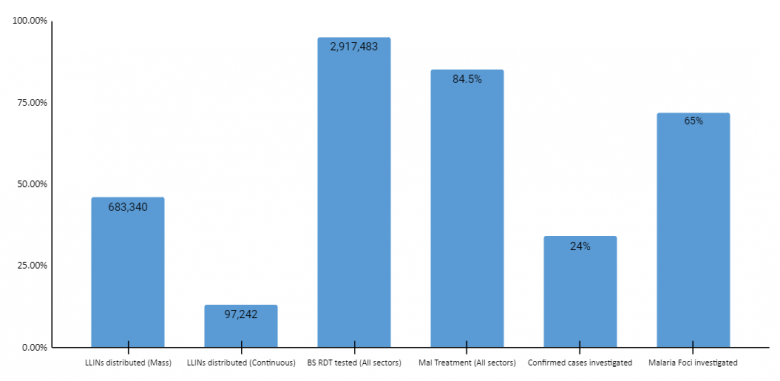
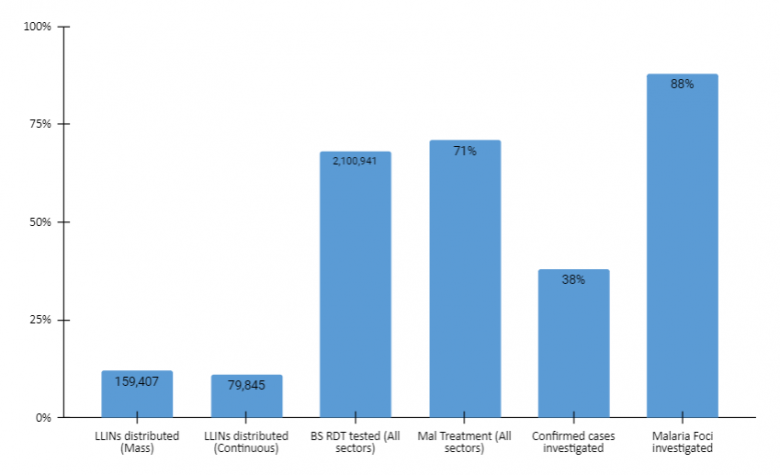
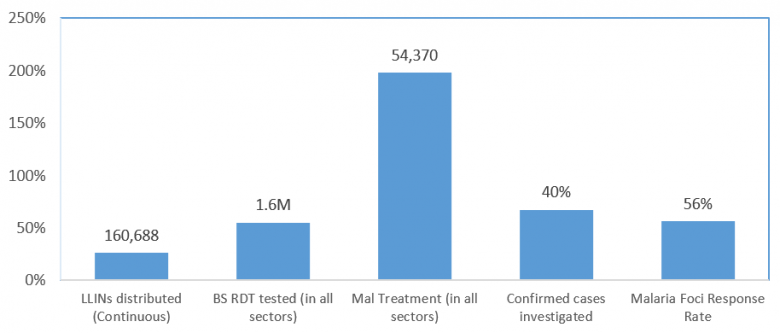
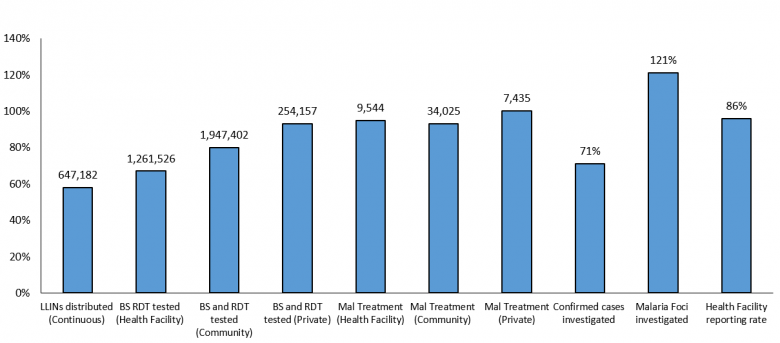
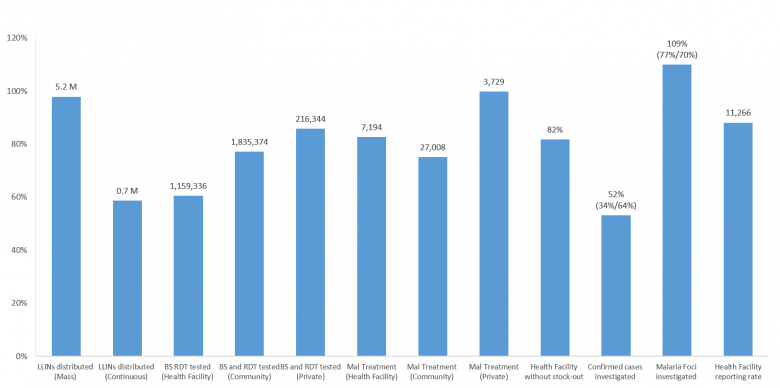
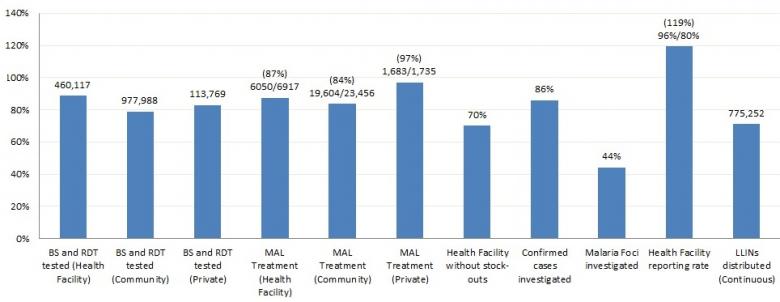
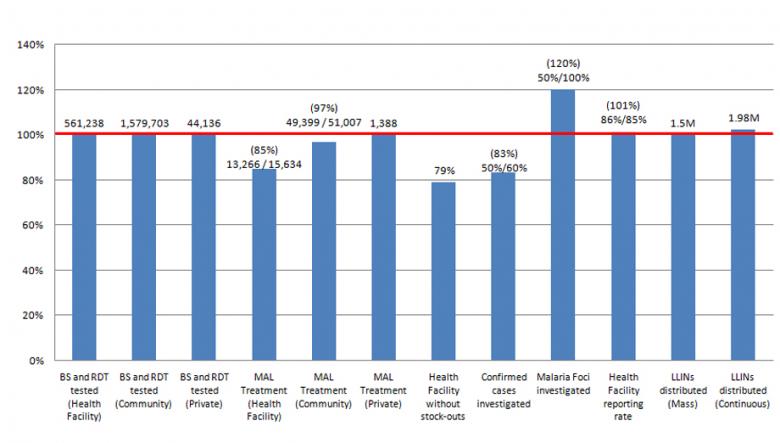
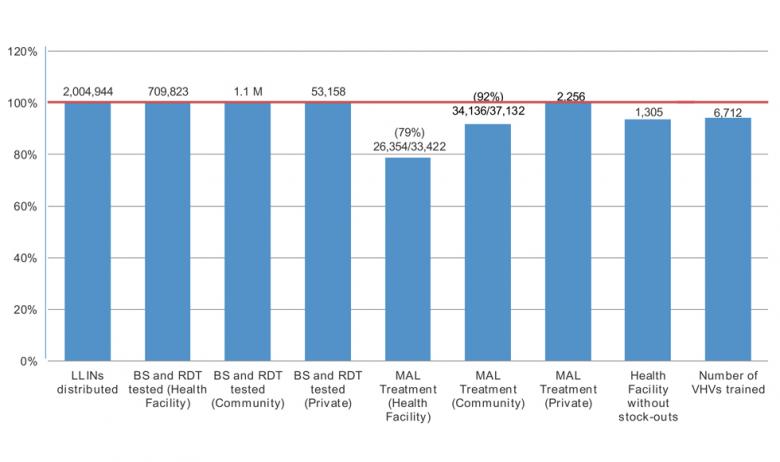
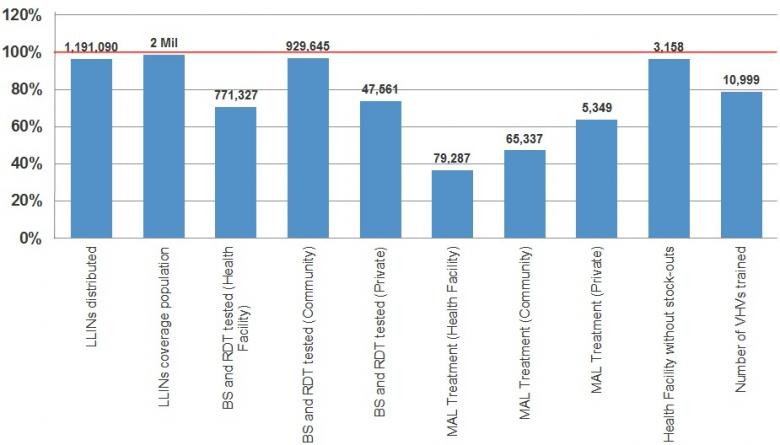
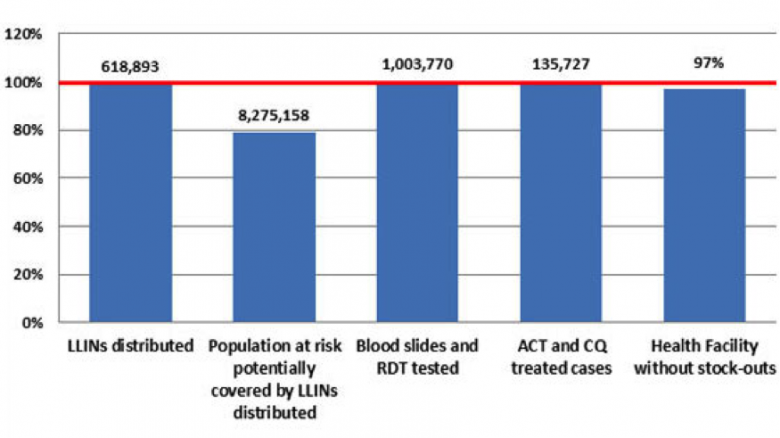
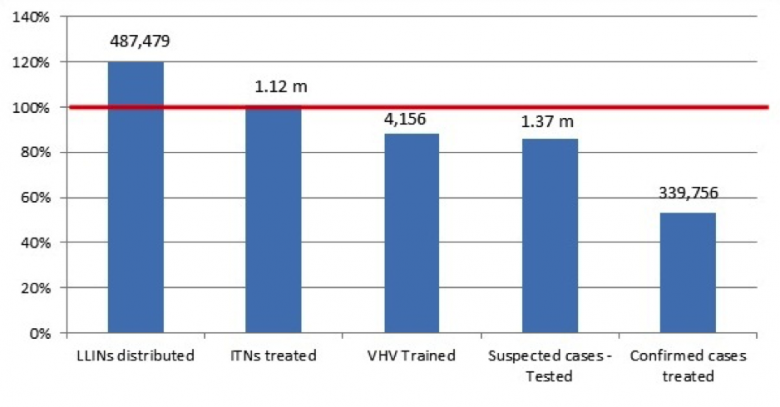
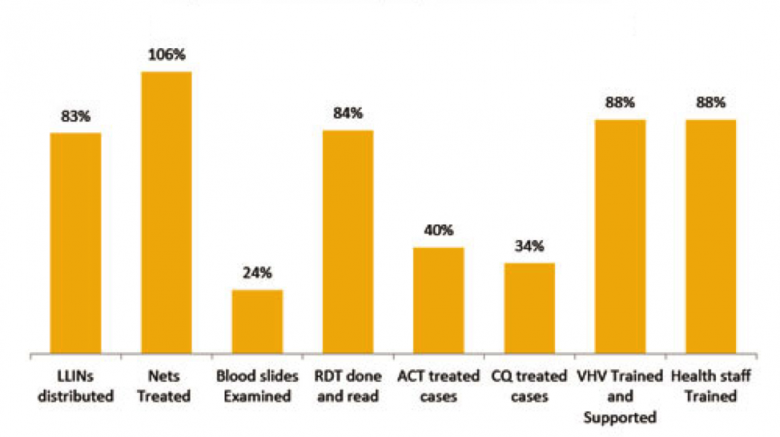
Malaria Programme at a glance
1. Goal:
To eliminate the indigenous transmission of Plasmodium falciparum (Pf) malaria by 2026 and put Myanmar on the path to eliminate all human malaria by 2030.
2. Target Group/Beneficiaries:
Malaria endemic populations:
- All villages, including those of ethnic minority groups;
- Communities close to forested areas;
- Internally displaced persons (IDP);
- Camps associated with large-scale construction projects (dams, bridges, mines, etc.);
- Settlements associated with plantations (rubber, oil palm, food);
- Seasonal agricultural laborers;
- Forest workers in the formal sector (police, border guards, forest/wildlife protection services) and informal sector (hunters, small-scale gem/gold miners, people gathering forest products such as precious timber, construction timber, rattan/bamboo);
- Transient or mobile camps associated with commercial projects (road/pipeline construction, large-scale logging, deep seaport projects);
- Formal and informal cross-border migrant workers.
3. Objectives:
- Achieve zero indigenous Pf malaria cases by 2026.
- Reduce all species malaria morbidity by 67% relative to the 2021 baseline figure and reduce mortality associated with indigenous malaria to zero by 2026.
- Prevent the re-establishment of indigenous transmission of Pf/all species malaria in townships where transmission has been interrupted.
- Prevent the emergence/introduction and spread of artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT) resistant Pf malaria in Myanmar.
4. Planned Activities:
- Case management through volunteers, public health facilities and private sector;
- Intensification Plan and Acceleration Strategies by Stratum
- Accelerator Strategy to accelerate Pf elimination including Mass Drug Administration, Targeted Drug Administration, and household active fever screening.;
- Activities specific for malaria elimination (including active case investigation, foci investigation and response);
- Vector control activities (including LLIN mass campaign, continuous LLIN distribution, entomological monitoring and Indoor Residual Spray (IRS));
- Vector control and case management activities targeting migrant, mobile, ethnic and vulnerable populations;
- Equitable access to malaria testing and treatment, particularly among the hardest-to-reach communities;
- Cross-border collaboration meetings;
- RSSH activities (case-based surveillance and reporting through an electronic reporting system as well as routine monitoring activities);
- Surveys such as community-based and operational research;
- Strengthening Integrated Drug Efficacy Surveillance (iDES) by collaborating with Department of Food and Drug Administration;
- Strengthening regional surveillance across GMS countries through a regional data-sharing platform.